A sore or painful tongue may be alarming but is usually not a cause for concern. Most instances of a sore tongue are minor problems that go away on their own or need minimal treatment.
Bites or injuries

A common cause of a sore tongue is accidentally biting the tongue when chewing food, or biting down suddenly.
Most people have experienced the sharp pain that comes from accidentally biting their tongue. Because the tongue shares mouth space with the teeth, it is not uncommon for a person to bite it while chewing.
The tongue can also become injured if the teeth clamp shut on it during an impact. This sometimes happens during contact sports or as a result of an accident, such as a slip or fall or a car accident.
Seizure disorders, such as epilepsy, can also result in tongue injuries, or lacerations when the teeth bite down on the tongue during a seizure.
It may take several days or more than a week for the sore spot to heal completely. Gargling a warm saltwater solution may help ease pain and aid with healing.
Severe bites or injuries to the tongue, however, may need medical attention.
Tongue injuries, or lacerations, are common in children. Deciding whether to repair them with stitches or surgery depends on the age of the child and the severity of the injury, according to a study in the International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.
If the injury looks deep or large or there is excessive bleeding, emergency care may be needed.
Oral thrush
The fungus Candida is present in the mouth, throat, and digestive tract. If the body is not able to keep the fungus in check and it overgrows, Candida causes a fungal infection. This happens more often in newborn babies and people with weakened immune systems.
When Candida overgrows in the mouth, this is known as oral thrush. It can cause painful yellow or white patches to form on the tongue and inside the mouth.
Treatment for thrush may include prescription antifungal medicines. It usually gets better about 2 weeks after a person starts the medication.
Canker sores
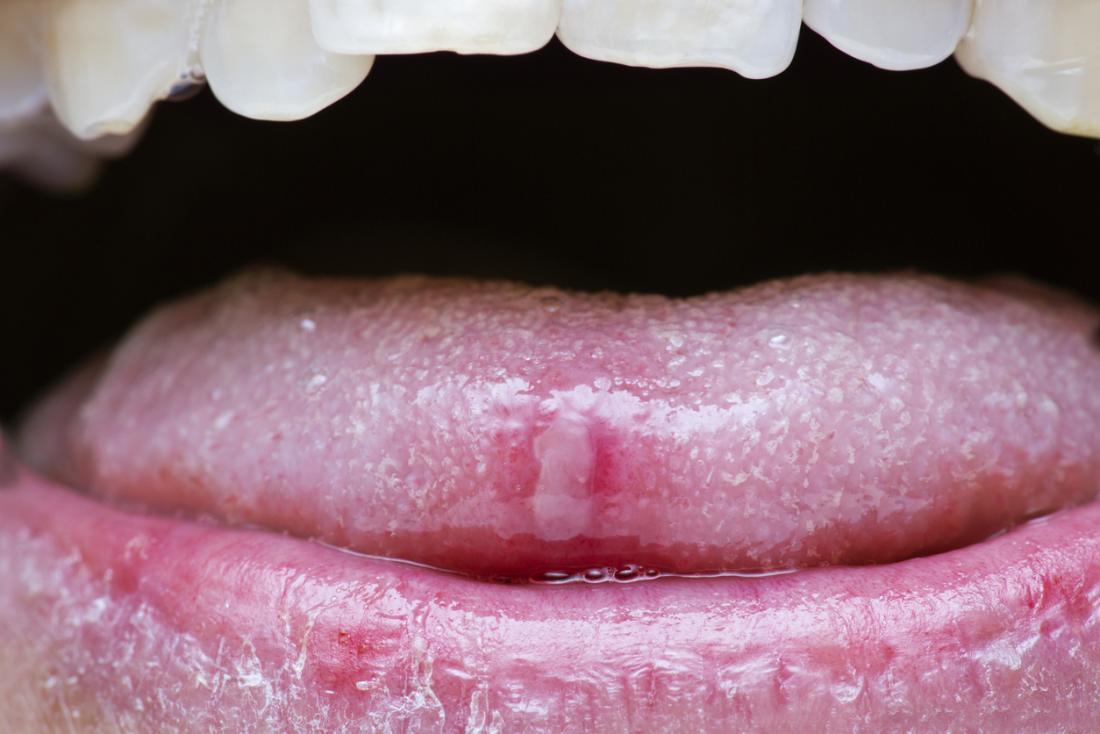
Canker sores are a painful type of spot that may occur inside the mouth. Usually, these will pass by themselves.
Most people have experienced a painful canker sore in the mouth. Known medically as aphthous ulcers, they may appear inside the lips or cheeks and under the tongue.
A canker sore looks like a small, round, white spot with a red border, and it can make eating or talking painful.
Experts do not know exactly what causes canker sores but think they may be due to:
- spicy or acidic foods
- emotional stress
- physical stress from an illness
- hormonal changes, especially in women
In most cases, canker sores will heal on their own. Treatments include over-the-counter topical pain medicines, saltwater rinses, or a prescription mouthwash.
If canker sores occur more than 3 times per year or cause significant pain, people should consult a doctor or dentist. Canker sores are not contagious.
Cold sores
Not to be confused with canker sores, cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus and are highly contagious. They are spread via skin-to-skin contact and appear as fluid-filled blisters that ooze and form a crust as they heal.
Even a person who does not have an active cold sore can spread it to others. Many children get cold sores from adults who may kiss them, share a drink or utensils with them, or touch their face.
Cold sores often appear on the outside of the mouth, but they can affect the tongue and cause pain, tingling, and burning.
Some doctors prescribe antiviral medicines to help lessen the severity of the sores and help them go away faster. Cold sores may return later, however, as the herpes virus never goes away once a person becomes infected with it.
Burning mouth syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome is a painful condition that causes a burning, numb, or tingling feeling on the tongue. The pain may last months or years, but the mouth will not have any visible problems, such as sores or redness.
Doctors cannot diagnose burning mouth syndrome during a mouth exam so they may have to base a diagnosis on symptoms alone.
It is not always possible to identify a cause, but burning mouth syndrome may be triggered by:
Treatment for this condition will depend on a person’s medical history and the severity of pain.
Glossitis
Glossitis means inflammation of the tongue. There are several different types of glossitis, but almost all of them can cause a sore or painful tongue.
Treatment varies, depending on the cause of the glossitis and the level of pain it causes.
Geographic tongue
The medical term for geographic tongue is benign migratory glossitis.
This condition occurs when the tiny, finger-like bumps on the tongue known as papillae disappear in small patches. This results in a smooth, red lesion on the tongue that is usually surrounded by a white border, giving the tongue a map-like appearance.
Some people experience a burning or painful sensation on the tongue. If this happens, topical numbing medications or prescription cortisone medicines may help with the pain.
The cause of geographic tongue is not known. There may be a link between geographic tongue and psoriasis, but people without psoriasis may still get geographic tongue. It is not contagious and does not lead to other health problems.
Median rhomboid glossitis
A smooth, red, flat area in the middle of the tongue is usually median rhomboid glossitis. It often causes no symptoms, so a person may not realize they have it unless a doctor or dentist finds it. It can, however, cause tongue pain, especially when eating certain foods.
Median rhomboid glossitis is thought to be caused by a fungal infection, so it is usually treated with antifungal medicine if the pain is bothersome. It is not contagious.
Other glossitis causes
The tongue can become inflamed and painful due to many different factors. Other common causes of glossitis include:
Allergic reactions
People who have a severe reaction to certain foods, insect bites, or other things may develop acute or sudden glossitis. This can cause swelling of the tongue, which may interfere with breathing.
Celiac disease
A study in Journal of Medical Case Reports found that atrophic glossitis was the only sign of celiac disease in some people.
Nutritional deficiencies, such as low iron or vitamin B-12
A study in the Journal of Oral Pathology and Medicine found “a significant association of deficiency of hemoglobin, iron, and vitamin B-12” with glossitis.
Similarly, a study in the Canadian Medical Association Journal discussed an individual who had a sore, burning tongue and was found to have a B-12 deficiency.
Tongue tumors
Any unexplained bleeding should be assessed by a medical professional.
A tumor on the tongue is another possible cause of a sore tongue. A tumor may appear as a sore spot, lump, or red or white patch on the tongue that does not go away.
Other symptoms that may accompany a tumor on the tongue include numbness, pain while swallowing, and unexplained bleeding.
Tumors can be either benign or cancerous. If anyone believes that they have a tumor on their tongue, they should see a doctor immediately.
Good oral health habits and tongue care
A sore tongue is usually not caused by oral care habits. However, keeping the mouth healthy and looking for any changes in the tongue’s appearance can be helpful in treating problems early.
Good oral care typically includes:
- brushing the teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- flossing at least once a day
- seeing a dentist at least every 6 months or as often as recommended
Brushing the tongue can help avoid bad-breath odor, but aggressive brushing or scraping is not necessary and can lead to irritation.
People should also avoid alcohol-based mouthwashes, especially if the tongue is sensitive or dry mouth is an issue.
Outlook
Though most tongue pain goes away without an issue, people should not ignore any changes in the tongue.
If a person experiences tongue pain does not have an obvious cause, they should consult a doctor or dentist. Tongue inflammation and pain can be a sign of an underlying condition or deficiency that needs treatment.
Let’s block ads! (Why?)





