
A dead tooth can be painful and change color.
Both tooth decay and an injury can cause a dead tooth. In this article, we look at the common symptoms, as well as how a dead tooth can be treated and prevented.
What is a dead tooth?
A tooth has three layers – enamel, dentin, and pulp. The pulp contains the blood vessels and nerves.
Dead or dying nerves in the pulp can lead to a dead tooth. A dead tooth will also no longer have any blood flow to it.
A dead nerve in a tooth is sometimes referred to as a necrotic pulp or a pulpless tooth.
Symptoms
It is not always easy to identify a dead tooth just by looking at it. Only a dental professional will be able to diagnose it, which is why regular trips to the dentist are important.
There are, however, two main symptoms of a dead tooth that can help with self-diagnosis:
- pain
- change in color
Pain
A tooth that is dead or dying can lead to a varying level of pain, from almost non-existent to extremely painful. The dying nerve or an infection usually causes an increase in pain.
Some people wonder why they experience pain if the nerve is dead. However, the pain is not coming from inside the tooth but from extremely sensitive nerve endings around the outside of the tooth, called the periodontal membrane.
Bacteria and dead nerve remnants, or pus, builds up in the pulp cavity inside the tooth and puts pressure on the periodontal membrane, which can cause immense pain.
If there is an infection, it may turn into an abscess and produce other symptoms, including:
- bad taste
- bad smell
- swelling
- a pimple on the gums
Change in color
If the tooth is dead, it will often get darker in color, and a person may notice a yellow, gray, or black discoloration.
A change in color usually occurs because the red blood cells are dying. This is a very similar effect to bruising.
The discoloration will usually happen if a dead tooth goes untreated and will increase over time.
Causes
There are two main causes of a dead tooth: tooth decay and tooth trauma.
Tooth decay
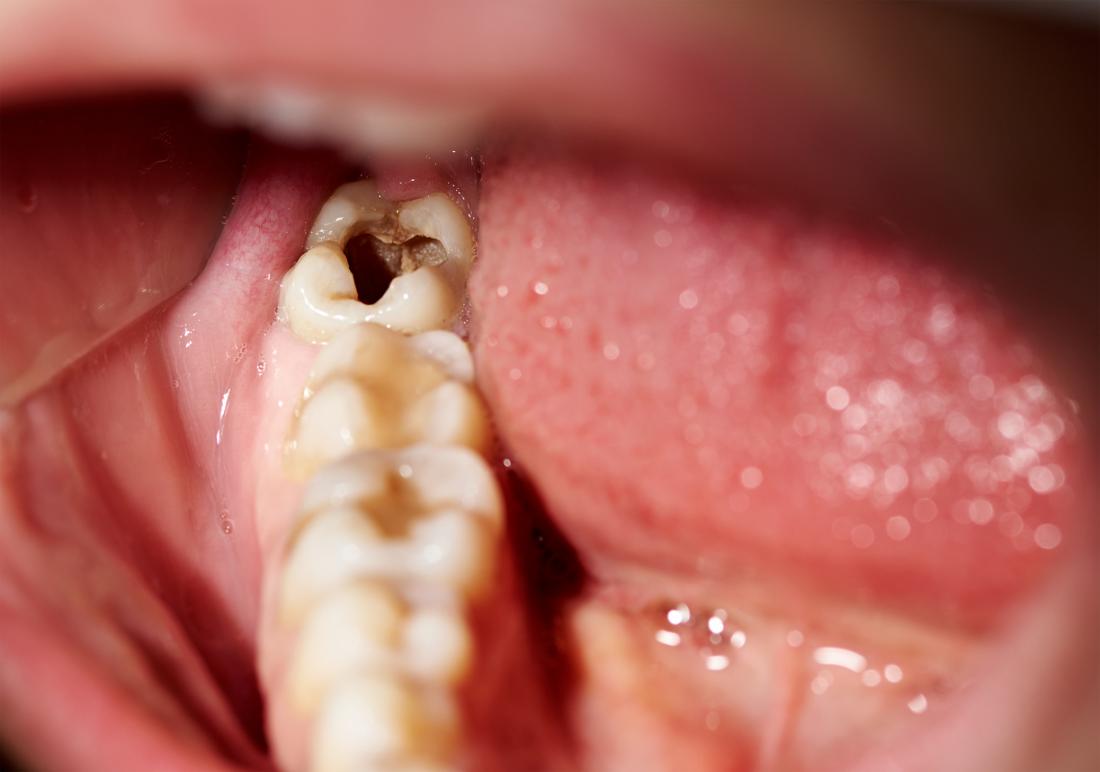
Tooth decay can lead to a dead tooth.
Tooth decay begins on the outermost layer of the tooth, but over time it can cause cavities that penetrate into the deeper layers.
If these cavities are left untreated, they can eventually reach the pulp and create a pathway for bacteria to enter the tooth and cause the nerve to die.
The healthy pulp will have an inflammatory response to the bacteria to try and fight off the infection, but the white blood cells can only hold it off for so long.
The pressure inside the pulp will increase, cutting off the blood supply, starving the nerve, and killing the pulp. This can cause intense pain.
Tooth trauma
If there is a physical trauma to the tooth, such as from a sports injury or a fall, then the blood vessels can burst, or the blood supply to the tooth may be cut off.
Eventually, because there is no blood flowing to the tooth, the nerve and other living tissues inside the pulp will die.
Treatment
Early treatment of a dead tooth is vital. If a bacterial infection is allowed to grow, it can move to the root of the tooth and start to attack the jawbone and other teeth.
Even if a person is not feeling pain at first, if they suspect they have a dead tooth they should seek medical advice as it could become extremely painful.
An X-ray will often help a dentist diagnose a dead tooth.
There are two options for treatment for a dead tooth:
- extraction or removal
- root canal
Extraction
If the dentist is unable to repair the tooth, they may have to remove it. This is one reason why early treatment is so important.
Tooth extraction is a simple procedure that is relatively cheap and painless. Later, a dentist can replace the tooth with a fixed bridge, implant, or another prosthetic tooth.
Root canal
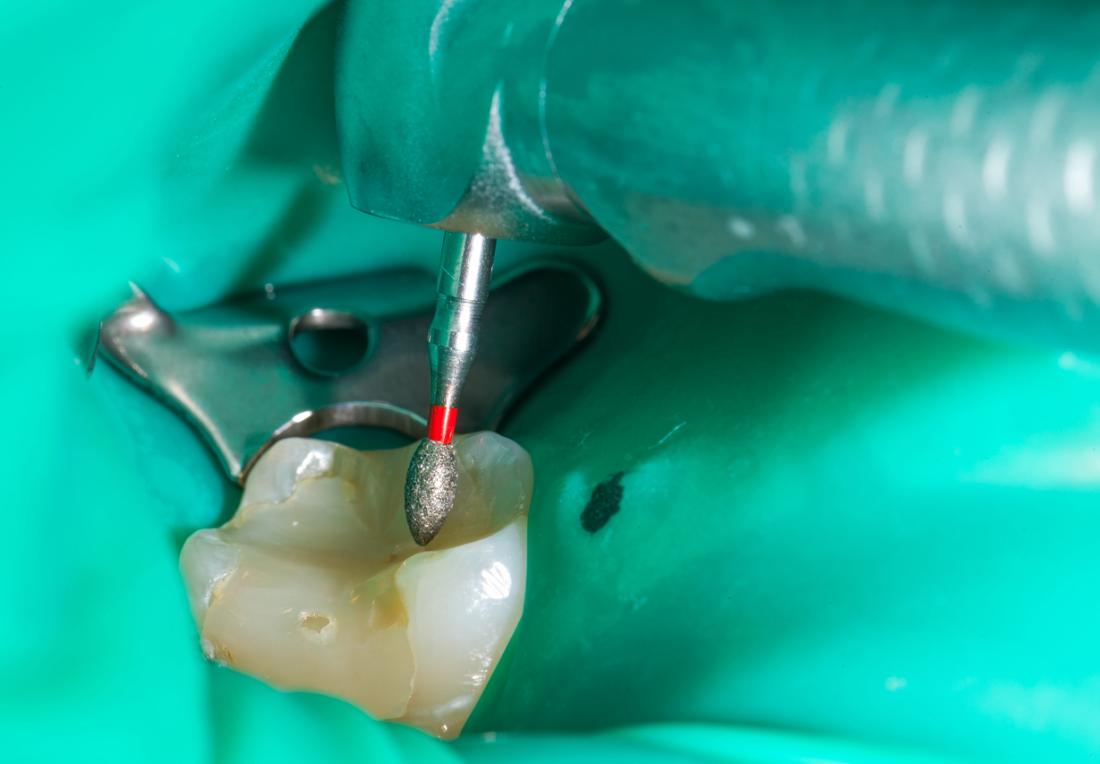
Root canal therapy may be used to treat a dead tooth.
Dentists avoid removing teeth if at all possible, so may recommend a root canal first.
Also known as endodontics, root canal treatment aims to clear all infection from the tooth and root. The area is then cleaned and sealed to try and prevent further infection.
Root canal treatment is a lengthy process, and the person will probably have to visit the dentist more than once before the treatment is complete.
Once the infection has cleared, the dentist will fill the tooth permanently. A dead tooth can still be functional after treatment, as most of the tooth is still intact.
However, because dead teeth can be more brittle, some people may need to have a crown fitted, which will provide extra support and strength to the tooth.
Prevention
The Oral Health Foundation recommend people follow a routine for dental care:
- brushing the teeth with fluoride toothpaste before bed and at least once more during the day
- cleaning between the teeth with floss or an interdental brush at least once a day
- avoiding sugary food and drinks
- having regular dental check-ups
Preventing tooth trauma is not always easy, although wearing a gum shield or mouth guard is recommended for people who do certain sports.
Also, a person should avoid chewing ice and opening things with their teeth. Individuals who grind their teeth at night might consider a mouth guard to use while they sleep as well.
Let’s block ads! (Why?)





